Introduction
1. Sometimes, it become essential to monitor physiological events from a distant place. Some of such situations are: (a) Monitoring of astronauts during flight. (b) Monitoring of patients in ambulance while transit to hospital. (c) Monitoring of patients while obtaining their exercise electrocardiogram. (d) Monitoring of patients who are permitted to stay away from the hospital. (e) Monitoring of animals in their natural habitat. (f) Transmission of ECG or other medical information through telephone links. (g) Isolating the patients from electricity operated measuring equipment such as ECG equipment in order to prevent any accidental shock to them.
2. Biotelemetry is a method of measuring biological paramenters from a distance. It is infact modification of existing methods of measuring physiological variables to a method of transmission of resulting data. The transmission of data from the point of generation to the point of reception can be done in various ways. The stethoscope is the simplest device which uses this principle of biotelemetry. The device amplifies acoustically the heartbeats and transmits their sound to the ears of a doctor through a hollow tube system. Certain applications of biotelemetry use telephone lines for transmission. However biotelemetry mainly uses radio transmission by suitably modifying the biological data. Earlier times, the telemetry could be applied to measure (1) temperature by rectal or oral thermistor (2) electrocardiograms by surface electrodes (3) indirect blood pressure by contact microphone and cuff (4) respiration by impedance pneumograph. However it is possible now to apply biotelemetry to almost all measurements such as (1) bioelectrical variables e.g. ECG, EMG and EEG and (2) physiological variables that require transducers e.g. blood pressure, blood flow and temperatures. The signal is obtained directly in electrical form in bioelectrical measurements require external excitation for the conversion of physiological variables into variations of resistance, induction or capacitance. The variations can be calibrated to display pressure, flow and temperature. In biotelemetry, the measurements as analog signals (voltage or current) in suitable form are transmitted which are received and decoded as actual measurements at the receiving end. ECG telemetry is the transmission of ECG, form site of an emergency to a hospital where a doctor can interpret, the ECG and instruct suitable treatment for the patient. Patients with heart problem can wear ECG telemetry unit on the job which relays ECG data to the hospital for checking. ECG telemetry unit is also used for monitoring when an athlete runs a race to improve his performance. Telemetry is also used for transmission of EEG. It is generally used for mentally disturbed children. The child wears specially designed the met known as football helmet or superman’s element which has built in electrodes so that his EEG a can be motored for any traumatic difficulty during play. Biotelemetry is also used for electromyogram (EMG) for studies of muscle damage or partial paralysis problem. Biotelemetry is commonly used in blood pressure, blood flow and heart rate research on unanaesthetised animals.
Biotelemetry System
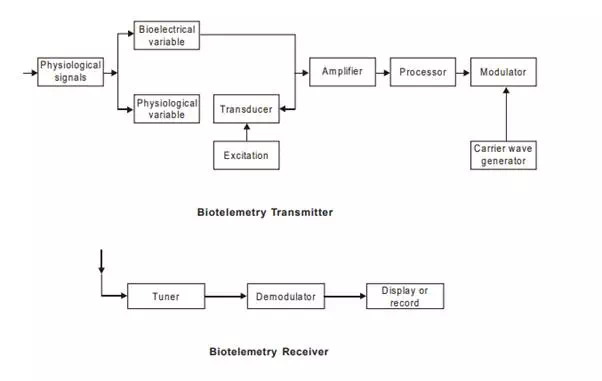
1. A biotelemetry system consists of transmitter and receiver. The functional blocks of a transmitter is as shown in the figure. Physiological signals are obtained by suitable transducer which are amplified and subjected to modulate the carrier waves for transmission. The receiver receives the transmission and demodulates to separates to separate the signal from the carrier waves to display or record the signal as shown in the block diagram.
Methods Of Modulation
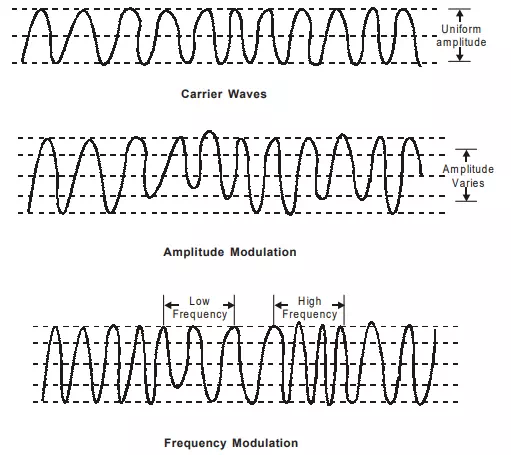
1. The modulation of carrier waves can be carried out either by amplitude modulation or by frequency modulation. In amplitude modulation, the amplitude of the carrier waves is caused to vary with the information signals being transmitted. In frequency modulation, the frequency of carrier wave is caused to very with the information signals being transmitted. Amplitude modulated transmission is susceptible to modulated transmission is less susceptible to electrical interference. The amplitudes and frequency modulation are as shown in the figure.
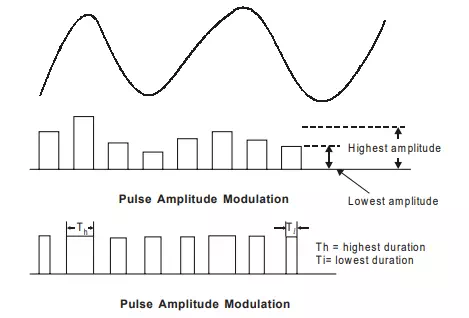
2. In case transmission carrier is in the form of pulses instead of sine waves, the technique of modulation is known as pulse modulation. If amplitude of the pulses is used to convey the transmitted information, the method is called pulse amplitude modulation (PAM). If the width of pulses is varied to convey transmitted information, the method is known as pulse width modulation (PWM).
Multiplexing
1. When many physiological signals are to be transmitted simultaneously, the method of frequency multiplexing is used. In this method, low frequency carrier waves (subcarrier) in audio frequency range are used. The subcarriers are modulated by the physiological signals which further modulate the RG carrier of the transmitter. Each physiological signal is placed on a subcarrier of a different frequency and all subcarriers Frequency multiplexing is more efficient and less expensive as compared to the method of employing separate transmitter for each physiological signal. At receiving end, transmission is received and demodulated to recover each of the separate subcarriers which are individually demodulated to retrieve original physiological signals.