Epithelial tissues are classified according to the shape of the cells and number of the cell layers formed . Cell shapes can be squamous (flattened and thin), cuboidal (boxy, as wide as it is tall), or columnar (rectangular, taller than it is wide). Similarly, the number of cell layers in the tissue can be one—where every cell rests on the basal lamina—which is a simple epithelium, or more than one, which is a stratified epithelium and only the basal layer of cells rests on the basal lamina. Pseudostratified (pseudo- = “false”) describes tissue with a single layer of irregularly shaped cells that give the appearance of more than one layer. Transitional describes a form of specialized stratified epithelium in which the shape of the cells can vary.
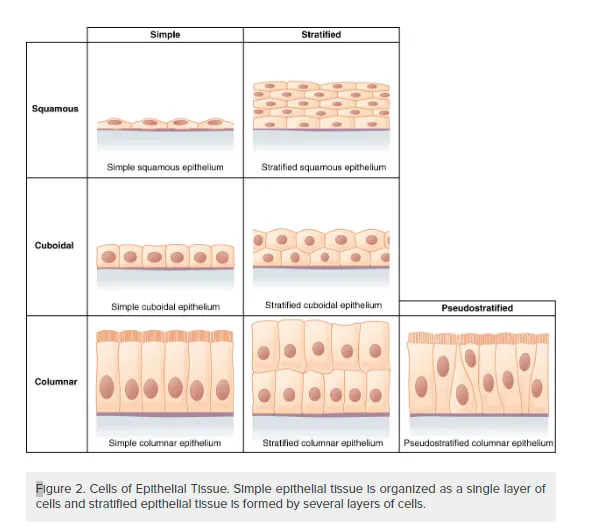
Figure 2. Cells of Epithelial Tissue. Simple epithelial tissue is organized as a single layer of cells and stratified epithelial tissue is formed by several layers of cells.
Simple Epithelium
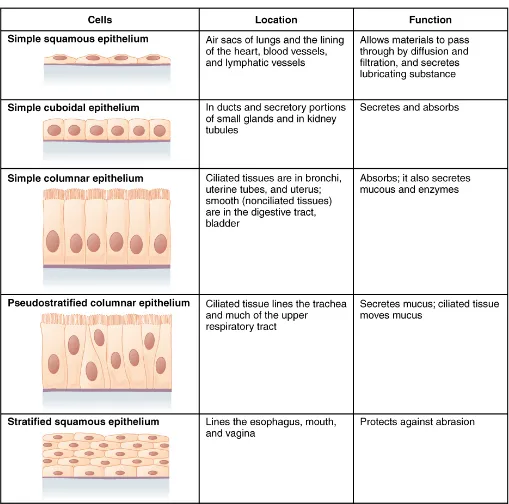
The shape of the cells in the single cell layer of simple epithelium reflects the functioning of those cells. The cells in simple squamous epithelium have the appearance of thin scales. Squamous cell nuclei tend to be flat, horizontal, and elliptical, mirroring the form of the cell. The endothelium is the epithelial tissue that lines vessels of the lymphatic and cardiovascular system, and it is made up of a single layer of squamous cells. Simple squamous epithelium, because of the thinness of the cell, is present where rapid passage of chemical compounds is observed. The alveoli of lungs where gases diffuse, segments of kidney tubules, and the lining of capillaries are also made of simple squamous epithelial tissue. The mesothelium is a simple squamous epithelium that forms the surface layer of the serous membrane that lines body cavities and internal organs. Its primary function is to provide a smooth and protective surface. Mesothelial cells are squamous epithelial cells that secrete a fluid that lubricates the mesothelium.
In simple cuboidal epithelium, the nucleus of the box-like cells appears round and is generally located near the center of the cell. These epithelia are active in the secretion and absorptions of molecules. Simple cuboidal epithelia are observed in the lining of the kidney tubules and in the ducts of glands.
In simple columnar epithelium, the nucleus of the tall column-like cells tends to be elongated and located in the basal end of the cells. Like the cuboidal epithelia, this epithelium is active in the absorption and secretion of molecules. Simple columnar epithelium forms the lining of some sections of the digestive system and parts of the female reproductive tract. Ciliated columnar epithelium is composed of simple columnar epithelial cells with cilia on their apical surfaces. These epithelial cells are found in the lining of the fallopian tubes and parts of the respiratory system, where the beating of the cilia helps remove particulate matter.
Pseudostratified columnar epithelium is a type of epithelium that appears to be stratified but instead consists of a single layer of irregularly shaped and differently sized columnar cells. In pseudostratified epithelium, nuclei of neighboring cells appear at different levels rather than clustered in the basal end. The arrangement gives the appearance of stratification; but in fact all the cells are in contact with the basal lamina, although some do not reach the apical surface. Pseudostratified columnar epithelium is found in the respiratory tract, where some of these cells have cilia.
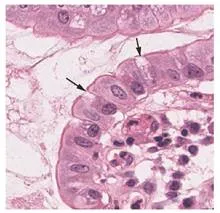
Both simple and pseudostratified columnar epithelia are heterogeneous epithelia because they include additional types of cells interspersed among the epithelial cells. For example, a goblet cell is a mucous-secreting unicellular “gland” interspersed between the columnar epithelial cells of mucous membranes (Figure 3).
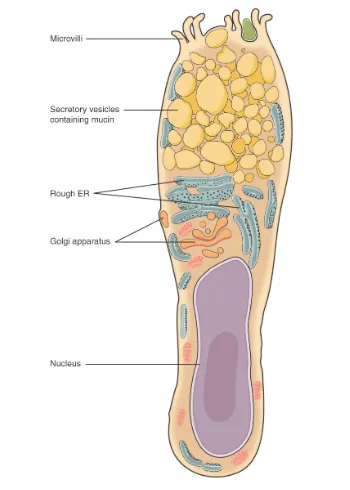
Figure 3. Goblet Cell. (a) In the lining of the small intestine, columnar epithelium cells are interspersed with goblet cells. (b) The arrows in this micrograph point to the mucous-secreting goblet cells. LM × 1600.
Stratified Epithelium
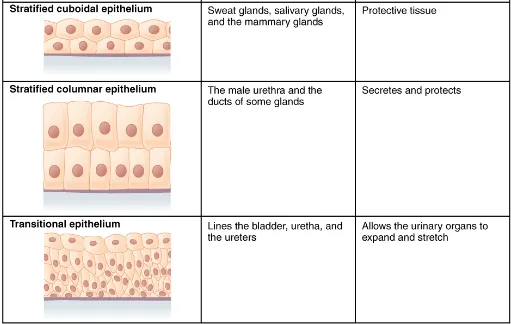
A stratified epithelium consists of several stacked layers of cells. This epithelium protects against physical and chemical wear and tear. The stratified epithelium is named by the shape of the most apical layer of cells, closest to the free space. Stratified squamous epithelium is the most common type of stratified epithelium in the human body. The apical cells are squamous, whereas the basal layer contains either columnar or cuboidal cells. The top layer may be covered with dead cells filled with keratin. Mammalian skin is an example of this dry, keratinized, stratified squamous epithelium. The lining of the mouth cavity is an example of an unkeratinized, stratified squamous epithelium. Stratified cuboidal epithelium and stratified columnar epithelium can also be found in certain glands and ducts, but are uncommon in the human body.
Another kind of stratified epithelium is transitional epithelium, so-called because of the gradual changes in the shapes of the apical cells as the bladder fills with urine. It is found only in the urinary system, specifically the ureters and urinary bladder. When the bladder is empty, this epithelium is convoluted and has cuboidal apical cells with convex, umbrella shaped, apical surfaces. As the bladder fills with urine, this epithelium loses its convolutions and the apical cells transition from cuboidal to squamous. It appears thicker and more multi-layered when the bladder is empty, and more stretched out and less stratified when the bladder is full and distended. Figure 4 summarizes the different categories of epithelial cell tissue cells.

Glandular Epithelium
A gland is a structure made up of one or more cells modified to synthesize and secrete chemical substances. Most glands consist of groups of epithelial cells. A gland can be classified as an endocrine gland, a ductless gland that releases secretions directly into surrounding tissues and fluids (endo- = “inside”), or an exocrine gland whose secretions leave through a duct that opens directly, or indirectly, to the external environment (exo- = “outside”).
Endocrine Glands
The secretions of endocrine glands are called hormones. Hormones are released into the interstitial fluid, diffused into the bloodstream, and delivered to targets, in other words, cells that have receptors to bind the hormones. The endocrine system is part of a major regulatory system coordinating the regulation and integration of body responses. A few examples of endocrine glands include the anterior pituitary, thymus, adrenal cortex, and gonads.
Exocrine Glands
Exocrine glands release their contents through a duct that leads to the epithelial surface. Mucous, sweat, saliva, and breast milk are all examples of secretions from exocrine glands. They are all discharged through tubular ducts. Secretions into the lumen of the gastrointestinal tract, technically outside of the body, are of the exocrine category.
Glandular Structure
Exocrine glands are classified as either unicellular or multicellular. The unicellular glands are scattered single cells, such as goblet cells, found in the mucous membranes of the small and large intestine.
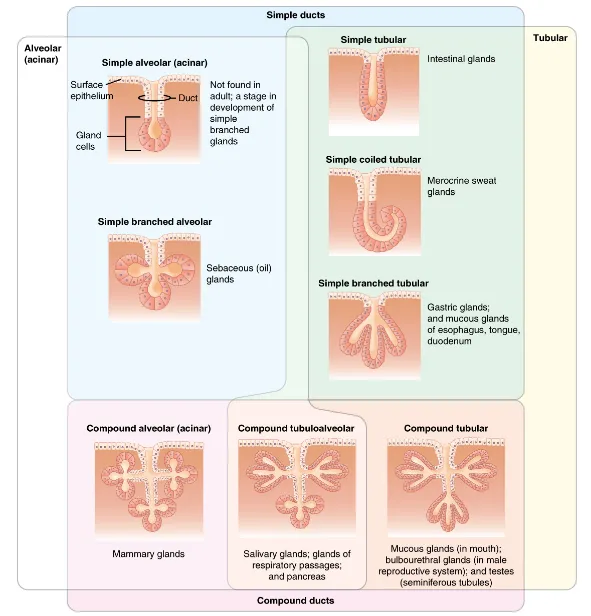
The multicellular exocrine glands known as serous glands develop from simple epithelium to form a secretory surface that secretes directly into an inner cavity. These glands line the internal cavities of the abdomen and chest and release their secretions directly into the cavities. Other multicellular exocrine glands release their contents through a tubular duct. The duct is single in a simple gland but in compound glands is divided into one or more branches (Figure 5). In tubular glands, the ducts can be straight or coiled, whereas tubes that form pockets are alveolar (acinar), such as the exocrine portion of the pancreas. Combinations of tubes and pockets are known as tubuloalveolar (tubuloacinar) compound glands. In a branched gland, a duct is connected to more than one secretory group of cells.

Methods and Types of Secretion
Exocrine glands can be classified by their mode of secretion and the nature of the substances released, as well as by the structure of the glands and shape of ducts (Figure 6). Merocrine secretion is the most common type of exocrine secretion. The secretions are enclosed in vesicles that move to the apical surface of the cell where the contents are released by exocytosis. For example, watery mucous containing the glycoprotein mucin, a lubricant that offers some pathogen protection is a merocrine secretion. The eccrine glands that produce and secrete sweat are another example.
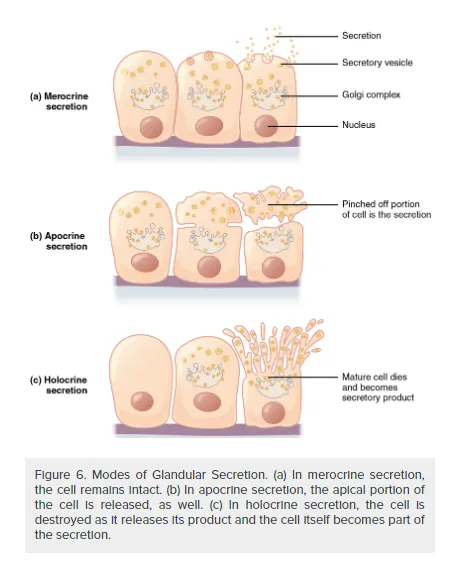
Apocrine secretion accumulates near the apical portion of the cell. That portion of the cell and its secretory contents pinch off from the cell and are released. The sweat glands of the armpit are classified as apocrine glands. Both merocrine and apocrine glands continue to produce and secrete their contents with little damage caused to the cell because the nucleus and golgi regions remain intact after secretion.
In contrast, the process of holocrine secretion involves the rupture and destruction of the entire gland cell. The cell accumulates its secretory products and releases them only when it bursts. New gland cells differentiate from cells in the surrounding tissue to replace those lost by secretion. The sebaceous glands that produce the oils on the skin and hair are holocrine glands/cells (Figure 7).
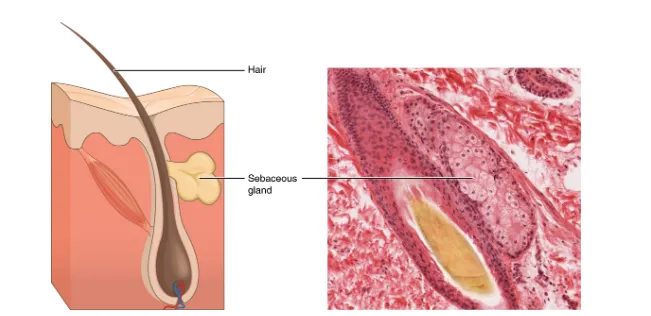
Figure 7. Sebaceous Glands. These glands secrete oils that lubricate and protect the skin. They are holocrine glands and they are destroyed after releasing their contents. New glandular cells form to replace the cells that are lost. LM × 400.
Glands are also named after the products they produce. The serous gland produces watery, blood-plasma-like secretions rich in enzymes such as alpha amylase, whereas the mucous gland releases watery to viscous products rich in the glycoprotein mucin. Both serous and mucous glands are common in the salivary glands of the mouth. Mixed exocrine glands contain both serous and mucous glands and release both types of secretions.
