Introduction
1. Telemedicine as name suggests, is the application of computer technology and telecommunication to provide health care from one place to another. Telemedicine uses information technology to provide timely treatment to those in need by telecommunication of the necessary expertise, diagnosis and information among distant located parties. Physicians, laboratories and patients can be distant located parties. Telecommunication enables all parties to interact as they are at one place, resulting in improved patient care and management, cost effectiveness and better utilisation of expertise. Telemedicine includes hardware, software, medical equipment and communication link.
Telemedicine Application
1. Telemedicine can be applied to all medical specialities, but its main applications are commonly found in pathology, cardiology, radiology and medical education. Telepathology is used to obtain an expert opinion on biopsy reports and microscopic photos of pathology slides. Teleradiology is used for telecommunication of radiology images like radiographs, CT scan, MRI and nuclear medicine from one place to another for expert interpretation and consultation. The problem faced in teleradilogy is the vast data associated with each image and lack of standardization of data for transmission. Telecardiology relates to telecommunication of ECG, echo cardiography and colour dopler of patient to experts for advice. Teleconsultation is used by the hospital or a patient to consult specialist doctors. Tele education can be used for providing medical education to junior doctors working at smaller towns who are professionally isolated from teaching hospitals. The block diagram of a typical telemedicine system is as shown in figure.

2. Telemedicine concepts can be : (a) Store and Forward : In this, information is compiled and stored. The stored information can be in the form of video images and clips or laboratory reports. The information in the digital form is stored and forwarded to the experts for interpretation and advice. The experts can access the same whenever possible and they can transmit back their advice. (b) Real time : In this, real time exchange of information takes place between two medical professionals or two centres. The real time exchange of information may be in the form of video conference or it may take place simultaneously with the examination and imaging of the patient.
Picture Archiving And Communication System
1. Integration of medical imaging devices and image processing facilities has firstly evolved picture archiving and communication system (PACS). Advancement in information technology has helped in transmission of medical images to one place to another and PACS has been suitably modified as shown in the figure. The imaging devices transmit the acquired.
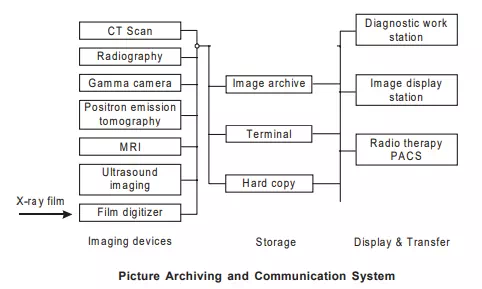
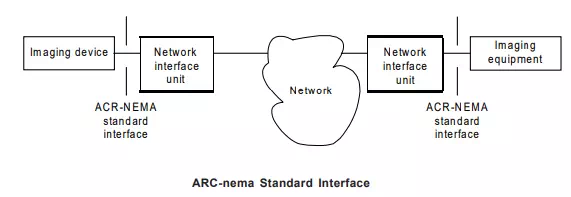
images through the network using a standardized transmission protocol. The images have to be compressed to reduce the data as well as their time for transmission. In order to avoid accidental erasing, digital images are stored on a medium capable of storing a large number of images in a read only memory as data base system to facilitate fast retrieval. Images can be viewed at any “image display station” or “diagnostic work station”. If required, algorithms can be applied to the ‘image data’ to enhance certain features or to interpreted the clinical information of the images. It is also possible to attach reports and comments to the images. A large number of methods are available for the transmission of images. Inside the hospital, local area network (LAN) is a good solution. However this has to done by compression of data through algorithms. This transfer requires compression and decompression algorithms as well as error detection and correction devices in the system. The transmission of images to remote places has another problem. There is complete lack of internationally accepted standard to code the images for transmission and also complete lack of a communication protocol for such coded images. The most appropriate communication protocol is likely to be “open systems interconnection” (OSI) being developed by ISO. The American college of Radiology (ACR) with the national electrical manufacturers Association (NOMA) have also prepared a standard for image format and for communication protocol for transmission of medical images.

The communication of medical images requires (1) an agreement on the format of representation of the digital image data (2) a communication protocol and (3) either LAN within the hospital or any other mean of communication to distant locations. The ACR-NEMA image format contains following information :
(a) identification data of the patient
(b) data of the examination and imaging device used
(c) image representation data
(d) image pixel data
Telemedicine By Mobile Communication
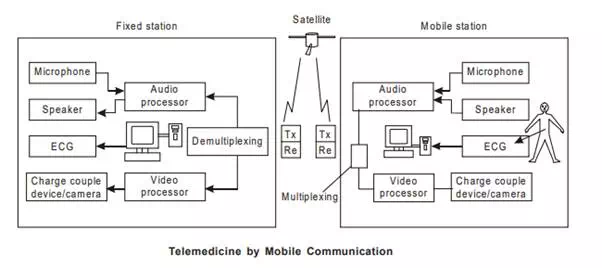
1. Mobile telemedicine is now possible using mobile communication and satellite communication as shown in the figure. In moving vehicle which has all necessary equipment, works as a mobile station. It obtains colour images, audio signal and physiological signals such as ECG and blood pressure etc. from the patient at the place of sickness which is far away from the health care centre. These are transmitted to the health care centre by the help of mobile communication. Multiplexing and demultiplexing is used to reduce the time for transmissions. The instruction for the suitable treatment is sent to the mobile station from the specialists at the fixed station.
Telemedicine And Internet
1. The world wide web (www) is an internet resource. It has information producing sites which can be accessed by the general public. It is possible to use the world wide web for imparting teleeduction and for other applications of telemedicine. However it is beneficial to have a dedicated link as it offers security to the data and reliability to communication due to fewer users using the link.
Medical Information System
1. Medical information systems (MIS) are being created on a department basis which as radiological information system (RIS) or on a hospital basis such as hospital information system (HIS). These information systems are created to contain and communicate patient data to any authorised user. It is of utmost importance that PACS should be integrated to RIS and HIS for effective utilization of all patient data.

Medical Coding And Classification
1. Medical coding and classification systems are expected to become increasingly important in the health care sector. They are integral part of the electronic health information systems. The coding and classification systems will be used to improve the quality and effectiveness of medical services. Activities connected to the different coding and classification systems are very important attempts at standardization which are taking place in different countries within the discipline of medical information. These activities must secure a proper professional and economic support. It is also of vital importance that national health authorities should participate in these activities so as to establish formal cooperation with professional bodies.
